As web developers, the best practices web development security should always be a top priority. With the increasing number of cyber threats, adopting robust security measures is essential, as the data comprises personal and financial information. Web apps must therefore continue to be safe and devoid of flaws that hackers could take advantage of.
The main factors for protecting a web application will be covered in this post. We will offer a list of ten enhancements that can assist guarantee the security of your online application, making it as focused as feasible. You may safeguard user data and guarantee the integrity of your web apps by adhering to these best practices and adopting a proactive approach to web application security.
Web Application Security Checklist: From 1 to 10
Web developers must incorporate web development security best practices from the start of their projects, since cyber threats are always changing. You may avoid expensive breaches, protect sensitive data, and guarantee a secure user experience by fixing vulnerabilities early on. This checklist offers a thorough manual to assist developers in building safe apps that withstand frequent attacks.
1. Secure Coding Practices: Input Validation and Sanitization
The cornerstone of creating web apps that are impervious to cyberattacks is secure code. You can reduce the possibility that vulnerabilities will be added to the application while it is being developed by writing secure code. To guarantee that your application is secure from the beginning, secure coding techniques should be applied consistently throughout the development lifecycle. Here are the examples.
Attackers frequently target user input. Always verify and clean inputs to avoid injection attacks (such as SQL injection, XSS, and command injection). Moreover, sanitization removes or encrypts hazardous characters, while validation ensures that input follows the required format, length, and type.
Furthermore, additional controls on the application’s front end and back end (server) are the best method to guarantee that input validation is consistent. Actually, it’s among the frontend web development security best practices. There are tools available in many frameworks and languages that make it simple for users to include this into their programming. For example, it is quite dangerous and might quickly expose you to a SQL injection attack if you are creating query strings in your code by just taking user input and sending it into a query.
2. Authentication and Authorization
The second enhancement on our list is to make sure that only authorized users access your application. For that purpose, we check which users have access. Therefore, we can drastically reduce the number of exploits that might otherwise be available to hackers.
Furthermore, establish safe password storage as part of the authentication process. Access to the program is no longer a barrier if attackers can simply get the passwords. Add multi-factor authentication to stop unwanted access to your web service. To ensure that the user is completely verified, a popular method is to send a login code via email or SMS to a trusted device.
Great authentication and access control standards can be attained in two ways:
- Saving passwords using secure hashing methods,
- Requiring frequent password changes.
Putting authentication techniques like biometrics and two-factor (2FA) into practice is the best mechanism to enhance authentication, authorization, and access control according to standards.
3. Data Protection: Encrypt Sensitive Data
Our next recommendation among web development security best practices is to use HTTPS and TLS encryption to ensure your apps are safe. Even for programs that don’t handle protected data or transactions, this method of web application access has become the norm. Many users, particularly those who handle sensitive data, anticipate that all websites will be secure.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure, or HTTPS for short, is a more secure version of the HTTP protocol. HTTPS uses Secure Sockets Layer (SSL), or Transport Layer Security (TLS), to create an encrypted connection between a web server and a client’s browser.
Moreover, with HTTPS, you can defend data in transit against interceptions and man-in-the-middle attacks. HTTPS can be used to restrict these kinds of assaults, which are easily carried out over insecure networks and connections. So, a lot of hosting options make it simple to deploy and maintain your apps with secure connections.
4. Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS)
Another simple method to reduce potential vulnerabilities is to make sure that only trusted domains access your services and resources. By setting up a CORS policy, your apps may determine which traffic to allow through and which to restrict based on its source.
Resources from other domains can be accessed or denied with the use of appropriate CORS headers. This lessens the likelihood of cross-site scripting and cross-site request forgery attacks. You can lower the danger of these kinds of attacks by appropriately defining CORS headers to limit access to your web application’s resources to trustworthy domains.
CORS capability is often integrated into frameworks, making it readily available and incredibly simple to set up. For instance, we may configure a CORS policy in Spring Boot as follows:
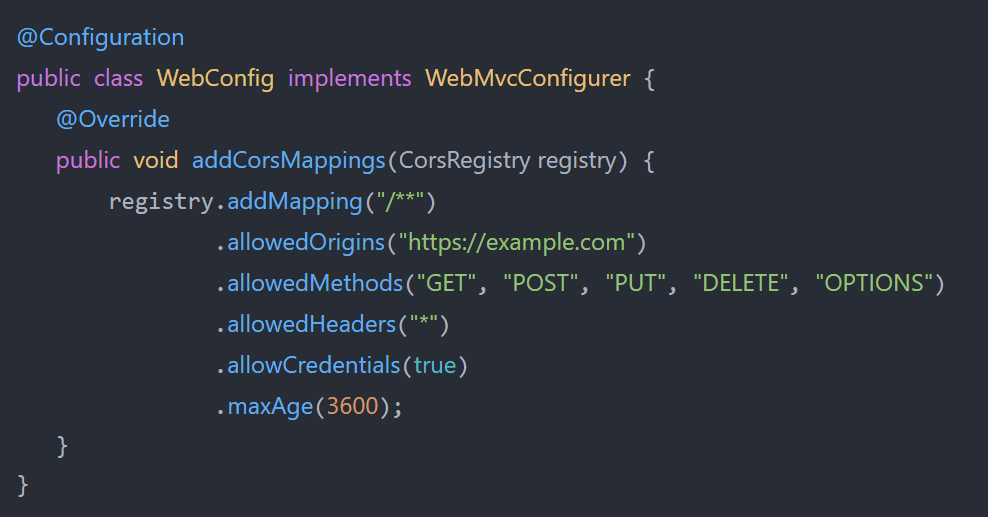
The following is stipulated by this example configuration:
- Enables the use of any of the HTTP methods GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and OPTIONS to access all resources from https://example.com.
- Any header in the request is permitted if the allowed headers value is *.
- Credentials can be sent in the request since the allowCredentials parameter is set to true.
- It is possible to cache the preflight answer for up to an hour, as shown by the maxAge value of 3600.
Your application can become much more secure by using even a basic configuration like the one shown above. As previously said, comparable configuration choices are available for numerous different frameworks.
5. Penetration Testing
Penetration testing of your application security measures is our fifth recommendation in the list of the web development security best practices. It is a technique that simulates a cyberattack to test the security of an application. It can be used to find security flaws and vulnerabilities in a web application that an attacker could take advantage of.
How is it conducted? A group of security professionals attempts to obtain unauthorized access to the online application and its data via certain tools and methods. All that they find can be used to address any vulnerabilities.
In practice, there are three types of penetration testing: white box, black box, and grey box. Giving complete access to system and network data, including login credentials, is a component of white box penetration testing. It saves time and money by enabling testers to mimic specific attacks using every attack vector that is accessible.
In black box penetration testing, the tester receives no information. This method requires the tester to act as an unprivileged attacker in order to mimic an external attack. It’s more expensive and time-consuming, and there’s a chance that insufficient information will cause vulnerabilities to go unnoticed.
Grey box penetration testing provides only limited access, including login credentials. By identifying possible vulnerabilities that a privileged user can exploit, this technique aids in fortifying safeguards to lessen the harm caused by such threats.
As a result of all three methods, your web application’s security is improved significantly.
6. Adopt a DevSecOps Approach
Including security specialists in the development process is a component of a DevSecOps methodology. At each level of the software development lifecycle, these professionals include security testing into the operations and development process. Instead of implementing security as an afterthought, DevSecOps seeks to include it in the online application from the beginning.
To avoid vulnerabilities, DevSecOps employs preventive measures against injection attacks, cross-site scripting, and the exposure of sensitive data as part of the best practices web development security. DevSecOps workflows can make use of a wide variety of tools. DevSecOps tool examples include:
- Tools for SAST (Static Application Security Testing),
- Dynamic Application Security Testing, or DAST,
- Tools for Container Security,
- Security Tools for Infrastructure as Code (IaC),
- Tools for Vulnerability Management,
- Tools for Secret Management.
Building and managing web apps may be made much more automated and secure with the help of the aforementioned tools. From checking for vulnerabilities in code and applications to making sure the infrastructure where the code is delivered is secure, these tools cover it all.
7. Secure Configuration and Deployment Practices
Maintaining the security of your web application depends on properly configuring and deploying it. This entails using secure coding techniques, protecting your database, and configuring your web server according to best practices.
Ensure that your team and organization have the necessary skill sets to manage a safe application deployment. This will also entail making sure that the procedures that will be taken and the deployment checklist are coordinated. Best practices for security should be considered at every stage.
It’s also critical to confirm that the database and server configurations are set up appropriately. It is important to ensure that servers are hardened and difficult for malicious actors to access. This should ideally be audited. For database servers that store sensitive data at rest, this is crucial.
The ability to implement best practices is embedded into a lot of servers and CI/CD pipelines. Make sure you read through and adhere to the suggested security setup as stated in the documents that the product’s makers have supplied.
8. OWASP’s Application Security Checklist
Ready for the next step as one of the best practices web development security? Your web application will be more secure and better defended against potential threats if you follow OWASP’s extensive list of security procedures. Numerous security precautions for your online application are covered by this checklist, such as input validation, error handling, encryption, authentication, and access controls. Developers may make sure they apply the most recent and efficient security measures by using this checklist.
All technical collaborators in a project should be made aware of the OWASP Application Security Checklist, even if many of the concerns are covered in this breakdown. This includes using the checklist as a guide to ensure that best practices are followed during code and deployment reviews.
9. Proper Logging Practices
In the case of a security breach, tracking and recording activity on your web application aids in spotting possible security risks and offers useful data for forensic investigations. Maintaining a thorough record of every application event makes it simple to follow an attacker’s movements and prevent subsequent exploits of the vulnerability.
Additionally, proper logging procedures make sure that external attackers cannot readily access logs. Attackers can use information in logs to plan an attack or spot vulnerabilities, just as internal investigators might use logs to determine how a breach happened.
Make sure that any sensitive information is hidden or left out of the log statements before pushing it to the logs. Sensitive information, such as passwords and credit card details, should never be included in a log file without first being masked. It could be just as harmful for an attacker to obtain a log containing this kind of information as it would be for them to gain access to the program itself.
Finally, make sure that statements from debug logs that output to a console or response are not moved into production code. They involve something as basic as a JavaScript file’s console.log, which may reveal a mistake that the attacker could take advantage of.
10. Use a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
By putting in place a web application firewall (WAF), you can defend your web application from frequent online threats. A well-configured WAF can easily fend off exploits, including denial of service assaults, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting. A WAF examines all incoming requests to your application and stops any nefarious ones.
WAFs can be a first line of defense for incoming traffic to the application and are rather easy to install, even though they are not a panacea against all web-based vulnerabilities. Many cloud providers offer a WAF as part of their stack if you are deploying your application on the cloud. You could utilize Cloudflare WAF or Wallarm Cloud WAF, to mention a couple, for something more independent of the platform you are deploying your app to.
Conclusion
Regularly reviewing and enhancing current security measures is necessary to guarantee the security of your online application. In addition to adhering to best practices for safe coding and deployment, this can involve input validation, authentication, access control, TLS, and CORS. Potential vulnerabilities can be found and fixed with the aid of technologies like StackHawk before attackers take advantage of them.
By following these web application development security best practices, you can reduce the risk of breaches and safeguard your web applications against a variety of threats. Remember, security is an ongoing process that requires continuous attention, updates, and staff education.